피에조 링은 주로 초음파 응용 분야에 사용되지만, 센서 및 액추에이터 조립에도 사용할 수 있습니다. 선택된 피에조 세라믹 소재는 응용 분야의 요구 사항에 따라 달라집니다. 다양한 셋업과 크기로 제작될 수 있습니다. 당사의 피에조 세라믹 링 제조 기술 포트폴리오는 다양한 용도로 활용이 가능합니다.
예를 들어, 산업용 초음파 용접, 드릴링 또는 세정 응용 분야에서는 강유전성 강질-PZT로 제작된 견고한 피에조 세라믹 링은 적층 구조로 사용합니다. 반면, 메쉬 네블라이저에서는 얇은 강유전성 연질-PZT 링을 금속 막에 접착하여 호흡기 질환 환자가 흡입할 수 있는 미세한 약물 입자를 생성합니다.
링은 디스크에 비해 결정적인 이점을 제공하는데, 장력 조절 나사를 조여 고정해 세라믹 소재에 기계적 예압을 가할 수 있습니다.
링을 개별적으로 더욱 정밀하게 가공하거나 링을 결합하여 변환기 트랜스듀서를 구성하는 것도 가능합니다. 특히 >> 고출력 초음파 트랜스듀서 조립 시 피에조 링은 에너지 효율적이고, 소형이며, 다용도로 활용 가능한 컴포넌트입니다. 설계에 따라 종방향 변위 외에도 비틀림 움직임을 구현할 수도 있습니다.
사양
30년 이상의 피에조 세라믹 개발 및 제작 경험을 바탕으로, PI Ceramic은 적합한 소재 선택에서부터 응용 분야 기반 솔루션 개발에 이르는 포괄적인 서비스를 제공합니다. 피에조 링의 데이터는 사양 제한 내에서 선택할 수 있습니다. 실현 가능성 확인을 위해 피에조 세라믹 링의 사양 또는 치수를 보내주시기 바랍니다.
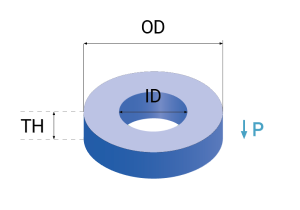
| 외경 OD[mm] | 1 - 150 |
| 내경 ID[mm] | 0.2 - 140 |
| 두께 TH[mm] | 0.15 - 30 |
| 전극 | 두꺼운 필름(Ag), 얇은 필름(Au, CuNi, Cu, NiV 등), 무전해 니켈 |
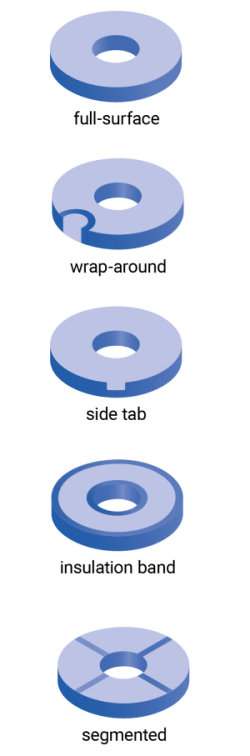
| 전극 설계 | 다양한 설계 중에서 선택 가능: 전체 면, 랩어라운드, 측면 탭, 절연 밴드, 분할(오른쪽 열 참조) |
| 분극 방향 | 피에조 컴포넌트의 설계에 따라 종방향, 반경 방향, 비틀림 또는 전단 방향으로 변위를 발생시킬 수 있습니다. 자세한 내용은 >> 작동 모드를 참조하세요. |
| 소재 | 당사는 다양한 강유전성 연질 및 강질 PTZ 소재와 무연 대체 소재를 제공합니다. 소재 개요는 >> 여기를 참조하세요. 데이터시트는 >> 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다. |
| 추가된 기능 | 조립 및 상호 연결 기술을 통한 고급 가공 외에도, 다음과 같이 즉시 설치할 수 있는 맞춤형 피에조 컴포넌트 개발도 가능합니다.
|
| 응용 분야 | 피에조 세라믹 링은 다양한 센서 및 액추에이터 응용 분야에 적합합니다. 잠재적인 사용 예시는 >> 여기에서 확인할 수 있습니다. |
작동 모드
피에조 세라믹 링을 센서로 사용할 때는 정압전효과의 원리를 따릅니다. 세라믹에 압력이나 초음파와 같은 기계적 부하가 가해지면, 피에조 컴포넌트는 전기 신호를 생성합니다.
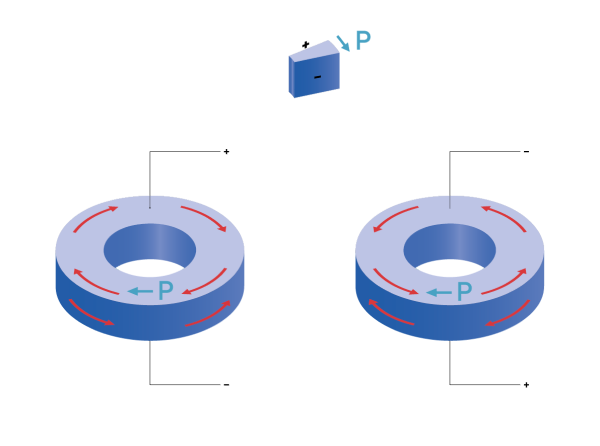
반면, 액추에이터로 사용될 경우 전압이 인가되면 피에조 링의 변위가 발생합니다. 이는 교류 전압으로 인해 초음파 영역 등에서 발생하는 진동에 의한 변형일 수 있습니다. 피에조 컴포넌트의 설계에 따라 종방향, 반경 방향, 비틀림 또는 전단 방향으로 변위를 발생시킬 수 있습니다. 변위량은 피에조 링의 크기와 가해진 전압에 의해 결정됩니다.
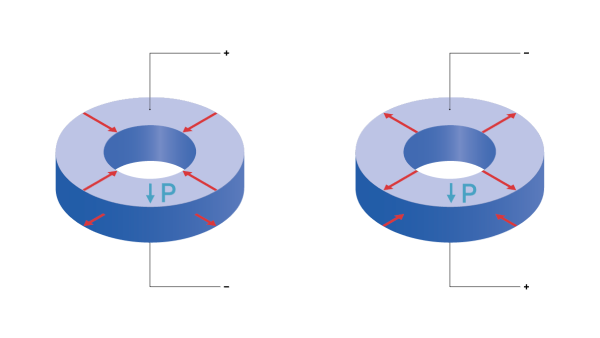
전체 면 전극을 가진 편광된 링에 대해서는 다음과 같은 변위 방향이 발생합니다.
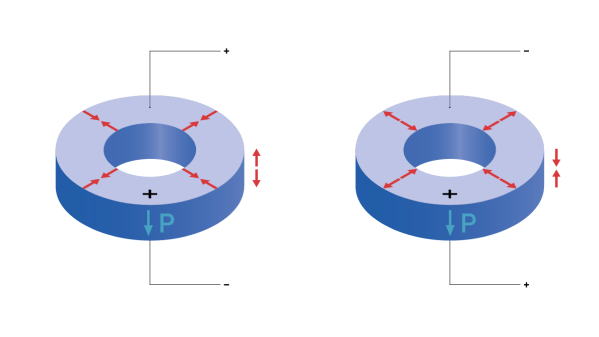
두께 방향으로 종방향 변위(33 효과)가 발생할 때마다 항상 반경 방향(31 효과)으로도 더 작은 변형이 함께 발생합니다.
종방향 진동 모드에서 특정 주파수에 도달하려면 링 두께를 변경해야 합니다. 반경 방향 주파수의 경우에는 직경을 조정해야 합니다. 두 가지 경우 모두 크기가 클수록 주파수는 낮아집니다.
전단 링과 비틀림 링은 특별한 제작 경로가 필요합니다. 설계에 따라 다음과 같은 변위가 발생할 수 있습니다.